معرفی شهر تولوز فرانسه (Toulouse)
 تولوز (Toulouse) شهری در جنوب غربی فرانسه بر ساحل رود گارون و یکی از مراکز صنایع پیشرفته اروپا است.
تولوز (Toulouse) شهری در جنوب غربی فرانسه بر ساحل رود گارون و یکی از مراکز صنایع پیشرفته اروپا است.این شهر در حد فاصل دریای مدیترانه و اقیانوس اطلس قرار گرفتهاست. فاصله این شهر تا پاریس ۷۳۰ کیلومتر است. تولوز چهارمین شهر بزرگ فرانسه و مرکز منطقه میدی پیرنه نیز میباشد.
در چند دهه گذشته، تولوز از خود نماد شهری فعال را به نمایش گذاردهاست. علاوه بر صنایع هوایی و فضایی مانند ایرباس، فعالیت در بخشهایی چون الکترونیک، صنایع پزشکی، علوم غذایی، فناوری اطلاعات، میکروبیولوژی و فناوری زیستی در جریان است که البته در گذشته نه چندان دور در بخش هایی مثل الکترونیک و الکتروتکنیک دانشکده برق آن جزو دانشکده های تراز اول اروپا محسوب می شد.
چنین رشد و پیشرفتی همواره در تعامل و همگونی با زندگی ساکنین بودهاست. این شهر میراث فرهنگی گذشته و حال خود را که دوستداران فراوان دارد، پاس میدارد.
در تولوز بیش از ۱۱۰٬۰۰۰ دانشجو در سه دانشگاه و چهارده موسسه آموزش عالی بزرگ مشغول به تحصیل هستند، این شهر رکورد بیشترین تعداد دانشگاههای شهرستانهای فرانسه را دارا است. شهر تولوز گنجینهای از میراث فرهنگی بی بدیل را در خود حفظ میکند، از جمله: موزهها، سالنهای نمایش و تئاترهای گوناگون.
جمعیت در سرشماری 2013 : 466,297 نفر
رتبه 4th in France
تراکم 3,900/km2
منطقهٔ زمانی CET (یوتیسی ۱+)
تابستان (DST) CEST (یوتیسی ۲+)
پیششماره(های) تلفن (۰۳۳)
وبگاه www.toulouse.fr
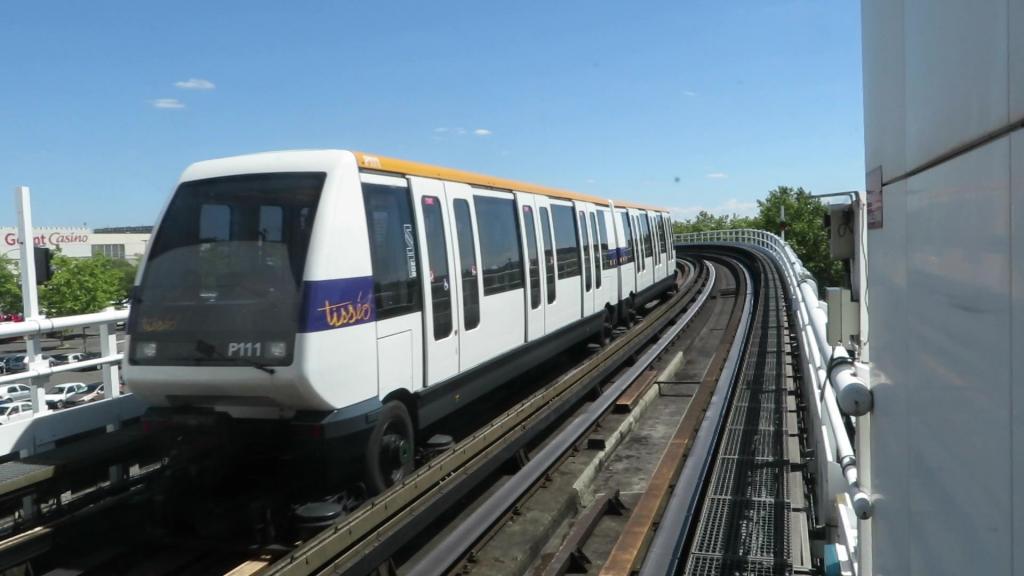

ترابری
متروی تولوز در سال ۱۹۹۳ تأسیس شده و هماکنون دارای ۲ خط و ۳۷ ایستگاه میباشد، همچنین تراموا این شهر در سال ۲۰۱۰ تأسیس شده که دارای ۲ خط و ۲۷ ایستگاه میباشد.

Toulouse is the capital of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the region of Occitanie. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, 150 kilometres (93 miles) from the Mediterranean Sea, 230 km (143 mi) from the Atlantic Ocean and 680 km (420 mi) from Paris. It is the fourth-largest city in France, with 466,297 inhabitants as of January 2014.
The Toulouse Metro area, with 1,312,304 inhabitants as of 2014, is France"s fourth-largest metropolitan area, after Paris, Lyon and Marseille, and ahead of Lille and Bordeaux.
Toulouse is the centre of the European aerospace industry, with the headquarters of Airbus (formerly EADS), the Galileo positioning system, the SPOT satellite system, ATR and the Aerospace Valley. It also hosts the European headquarters of Intel and CNES"s Toulouse Space Centre (CST), the largest space centre in Europe. Thales Alenia Space, and Astrium Satellites also have a significant presence in Toulouse.
The University of Toulouse is one of the oldest in Europe (founded in 1229) and, with more than 103,000 students, it is the fourth-largest university campus in France, after the universities of Paris, Lyon and Lille.
The air route between Toulouse–Blagnac and Paris Orly is the busiest in Europe, transporting 2.4 million passengers in 2014. According to the rankings of L"Express and Challenges, Toulouse is the most dynamic French city.
The city was the capital of the Visigothic Kingdom in the 5th century and the capital of the province of Languedoc in the Late Middle Ages and early modern period (provinces were abolished during the French Revolution), making it the unofficial capital of the cultural region of Occitania (Southern France). It is now the capital of the Occitanie region, the largest region in Metropolitan France.
A city with unique architecture made of pinkish terracotta bricks, which earned it the nickname la Ville Rose ("the Pink City"), Toulouse counts two UNESCO World Heritage Sites, the Canal du Midi (designated in 1996 and shared with other cities), and the Basilica of St. Sernin, the largest remaining Romanesque building in Europe, designated in 1998 because of its significance to the Santiago de Compostela pilgrimage route.

Early history
The Garonne Valley was a central point for trade between the Pyrenees, the Mediterranean and the Atlantic since at least the Iron Age. The historical name of the city, Tolosa (Τώλοσσα in Greek, and of its inhabitants, the Tolosates, first recorded in the 2nd century BC), it is of unknown meaning or origin, possibly from Aquitanian, or from Iberian, but has also been connected to the name of the Gaulish Volcae Tectosages.
Tolosa enters the historical period in the 2nd century BC, when it became a Roman military outpost. After the conquest of Gaul, it was developed as a Roman city of Gallia Narbonensis. In the 5th century, Tolosa fell to the Visigothic kingdom and became one of its major cities, in the early 6th century even serving as its capital, before it fell to the Franks under Clovis in 507 (Battle of Vouillé). From this time, Toulouse was the capital of Aquitaine within the Frankish realm.
In 721, Duke Odo of Aquitaine defeated an invading Umayyad Muslim army at the Battle of Toulouse. Odo"s victory was a small obstacle to Muslim expansion into Christian Europe, and Muslims finally occupied a large territory including Poitiers. Charles Martel, a decade later, won the Battle of Tours, also called the Battle of Poitiers.
The Frankish conquest of Septimania followed in the 750s, and a quasi-independent County of Toulouse emerged within the Carolingian sub-kingdom of Aquitaine by the late 8th century. The Battle of Toulouse of 844, pitting Charles the Bald against Pepin II of Aquitaine, was key in the Carolingian Civil War.
County of Toulouse
During the Carolingian era, the town rose in status, becoming the capital of the County of Toulouse.
In the 12th century, consuls took over the running of the town and these proved to be difficult years. In particular, it was a time of religious turmoil. In Toulouse, the Cathars tried to set up a community here, but were routed by Simon de Montfort"s troops. The Dominican Order was founded in Toulouse in 1215 by Saint Dominic in this context of struggle against the Cathar heresy. The subsequent arrival of the Inquisition led to a period of religious fervour during which time the Dominican Couvent des Jacobins was founded. Governed by Raimond II and a group of city nobles, Toulouse"s urban boundaries stretched beyond its walls to the north and as far south as Saint Michel.
In the Treaty of Paris of 1229, Toulouse formally submitted to the crown of France. The county"s sole heiress Joan was engaged to Alphonse, Count of Poitiers, a younger brother of Louis IX of France. The marriage became legal in 1241, but it remained childless so that after Joan"s death the county fell to the crown of France by inheritance. Also in 1229, University of Toulouse was established after the Parisian model, intended as a means to dissolve the heretic movement.
Various monastic orders, like the congregation of the order of frères prêcheurs, were started. They found home in Les Jacobins. In parallel, a long period of inquisition began inside the Toulouse walls. The fear of repression obliged the notabilities to exile, or to convert themselves. The inquisition lasted nearly 400 years, making Toulouse its capital. Count Raimond VII was convicted of heresy and died in 1249 without an heir.
Within the Kingdom of France
In 1271, Toulouse was incorporated into the kingdom of France and declared a "royal city". With this accolade, it started to transform itself into an intellectual and artistic centre. In 1323 the Consistori del Gay Saber was established in Toulouse to preserve the lyric art of the troubadours. Toulouse became the centre of Occitan literary culture for the next hundred years; the Consistori was last active in 1484.
But the 14th century was to mark a downturn in the city"s fortunes. First came a pogrom against Toulouse"s Jewish population by Crusaders in 1320, then, in 1348, the Black Death, then the Hundred Years" War. Famine and floods also took their toll on the city. Despite strong immigration, the population lost 10,000 inhabitants in 70 years. By 1405 Toulouse had only 19,000 people.
It was not until the 15th century that Toulouse started to prosper. Reinforcing its place as an administrative center, the city grew richer, participating in the trade of Bordeaux wine with England, as well as cereals and textiles. A parliament was set up by Charles VII and the city"s merchants grew ever wealthier. Their economic well-being was mostly based on a plant-based blue dye known as pastel, made from woad, which they exported throughout Europe. These pastel merchants built grand town houses and, before long, both architecture and the fine arts flourished in the city as never before.
The bubble finally burst in the mid-16th century. Another blue dye arrived from India, known as indigo. It wiped out the pastel trade in one fell swoop. Religious conflict broke out between the Catholics and the Protestant Calvinists. At the same time, buildings were destroyed by fire and there were yet more outbreaks of famine and plague.
In 1761, a Toulouse merchant, Jean Calas, was accused of murdering his own son to prevent his conversion to Catholicism. Calas was put to death a year later. Toulouse"s persecution of Protestants such as Calas was widely condemned and religious intolerance did gradually disappear.
During the remainder of the 18th century, the city was slowly modernised. This included a period of urban rebuilding, which began in earnest from 1750. New projects included the building of the Jardin Royal. The Grand Rond also dates to this period, along with the Canal de Brienne and the Quai Dillon.


